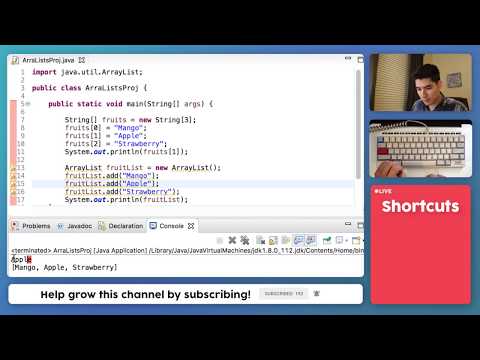
Searches this list or its range for an element having the key returned by the specified selector function equal to the provided key value using the binary search algorithm. The list is expected to be sorted into ascending order according to the Comparable natural ordering of keys of its elements. In Python 2 filter would have returned a list already checking all the values of the original list. The filter function in Python 3 returns a filter object and only executes the filtering condition when the user actually wants to find the next element in the filtered list. Random access means that we can grab any element at constant time. Unlike simple arrays, anArrayList can hold data of multiple data types.
Master in Python Programming Certification is one of the most sought after certifications in the market. The reason for this is the array of functionalities Python offers. Lists are one collection that simplifies the life of programmers to a great extent. In this article, we shall learn one such feature that is how to remove elements from lists. After remove is invoked on a generated iterator, the removed element will no longer appear in either that iterator or any other iterator created from the same source iterable. That is, this method behaves exactly as Iterables.cycle(Lists.newArrayList).
The iterator's hasNext method returns true until all of the original elements have been removed. The example adds five different data types into an array list — a string, double, integer, object, and enumeration. Returns a view of unfiltered containing all elements that satisfy the input predicate retainIfTrue. The returned iterable's iterator does not support remove(). Some list implementations have restrictions on the elements that they may contain.
For example, some implementations prohibit null elements, and some have restrictions on the types of their elements. Attempting to add an ineligible element throws an unchecked exception, typically NullPointerException or ClassCastException. Such exceptions are marked as "optional" in the specification for this interface. This snippet will find the first element in arraylist using java 8. The Java 8 Streams API provides Streams.findFirst which will return the wrapper Optional object describing the first element of the stream.
If the arraylist is empty, an empty Optional will be returned. Another way that is more compact and some people might find nicer is to use the filter function of Python. Usually we use it to create a shorter list of elements meeting some condition.
In this case however we don't need to store the result of the filter call in a variable. This will return the next element returned by the filter object. Which, in our case, will be the first element in the list. These will have "collection" type in the template language, which is like a restricted sequence. Returns a view of unfiltered containing all elements that are of the type desiredType.
Enumerate() function is a built-in function available with python. You can make use of enumerate to get all the indexes of the element in a list. It takes input as an iterable object (i.e., an object that can be looped), and the output is an object with a counter to each item. A list is a container that stores items of different data types (ints, floats, Boolean, strings, etc.) in an ordered sequence. It is an important data structure that is in-built in Python. The data is written inside square brackets ([]), and the values are separated by comma.
It will remove multiple elements from a list if we provide an index range. To remove multiple elements from a list in index positions 2 to 5, we should use the del method which will remove elements in range from index2 to index5. Mutating values returned by the view is highly discouraged because success of the operation directly depends on the type of the map being manipulated. In particular, Groovy relies on collections from the JDK that in general make no guarantee that a collection can safely be manipulated through keySet, entrySet, orvalues. Groovy provides native support for various collection types, including lists,maps or ranges.
Most of those are based on the Java collection types and decorated with additional methods found in the Groovy development kit. Returns a list of values built from the elements of this collection and the other array with the same index using the provided transform function applied to each pair of elements. The returned list has length of the shortest collection.
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence ; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. If the list fits in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and the size of this list. I looped through each at the same time and add the current value to a separate set for each of the lists. Also, check if the current element is already in the other list's set.
Furthermore the result of filter is then a collection, not a sequence, therefor sequence operations (like seq) will not work on it. Determines whether two iterables contain equal elements in the same order. With the stream method, we create a stream from a list.
Thesorted method sorts elements according to the provided comparator. With Integer.compare we compare the populations of countries. With collect, we transform the stream into a list of countries. The remove() method removes the first matching element from the list. The pop() method removes an element at a given index, and will also return the removed item. You can also use the del keyword in Python to remove an element or slice from a list.
In the following example we have an arraylist of strings and we have added few elements to the arraylist. Here we are using the indexOf() method to find the index of few specified elements in the ArrayList. The shift method removes the element at the zeroeth index and shifts the values at consecutive indexes down, then returns the removed value.
The shift() method removes the firstelement from an array and returns that removed element. Returns a list of all elements sorted descending according to natural sort order of the value returned by specified selector function. Returns a list of all elements sorted according to natural sort order of the value returned by specified selector function. Returns a list containing only elements from the given collection having distinct keys returned by the given selector function. Searches this list or its range for the provided element using the binary search algorithm.
The list is expected to be sorted into ascending order according to the Comparable natural ordering of its elements, otherwise the result is undefined. A stream provides an interface to a sequenced set of values of a specific element type. However, stream consumes data from the source such as Collection List or Set as shown in the example above.
Note, Collection.stream() creates as sequential stream and Collection.parallelStream() creates a parallel stream. (T[] a)Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper sequence ; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. The List interface provides four methods for positional access to list elements. Note that these operations may execute in time proportional to the index value for some implementations . Thus, iterating over the elements in a list is typically preferable to indexing through it if the caller does not know the implementation. Whichever is smaller in length, loop through it and put it's elements in a LinkedHashSet (it doesn't matter if it's sorted or unsorted).
Then loop through the second array and query the set for that element. If the problem is to find the first element of list L1 which is also contained in L2, run through the elements of L1 one-by-one and check if the current element is in L2. The second test ("is element in L2") can be either done by a simple loop over all elements in L2. Or you put all elements of L2 into a hashset first, which can speed-up the process fairly.
If you are a Java programmer, note how the filter built-in differs from Java Stream.filter. Stream.filteris "lazy", while FreeMarker filteris basically "eager", and is only "lazy" in special cases, and within a limited scope. Thus, unlike in Java, calling filter is not always free. In particular, if you assign a filtered sequence to a variable, or pass it to a custom directive/function/method, the filtered sequence will be created eagerly. Returns a view of iterable containing its first limitSizeelements.
If iterable contains fewer than limitSizeelements, the returned view contains all of its elements. The returned iterable's iterator supports remove() if iterable's iterator does. Divides an iterable into unmodifiable sublists of the given size, padding the final iterable with null values if necessary. Iterators returned by the returned iterable do not support the Iterator.remove() method.
The returned lists implement RandomAccess, whether or not the input list does. The returned iterable's iterator supports remove() when the corresponding input iterator supports it. The methods of the returned iterable may throw NullPointerException if any of the input iterators is null. This class contains static utility methods that operate on or return objects of type Iterable. Except as noted, each method has a corresponding Iterator-based method in the Iterators class.
The removeAll method removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection. The removeIf method removes all of the elements of a collection that satisfy the given predicate. The simplest approach is to use list's pop() method which removes and returns an item present at the specified position in the list. As you can see, all the elements are enclosed within square brackets i.e. and each element is separated by a comma. This list is an ordered sequence that contains elements of different data types.
Method removes the first element of the array and returns it. List in Scala is a collection that stores data in the form of a linked-list. The list is an immutable collection which means the elements of a list cannot be altered after the list is created. We can access elements of the array using the index of the element.
The following statement returns -1 even though the first element of the guests array and the searchElement have the same values in the name and ages properties. Returns the smallest value among all values produced by selector function applied to each element in the collection or null if there are no elements. Returns the largest value among all values produced by selector function applied to each element in the collection or null if there are no elements. The list is expected to be sorted into ascending order according to the specified comparator, otherwise the result is undefined.
Populates and returns the destination mutable map with key-value pairs provided by transform function applied to each element of the given collection. This tutorial explains you how to find first element from collection like List or Set using Java 8 streams findFirst(), iterator() and listIterator methods. Lists that support this operation may place limitations on what elements may be added to this list.
In particular, some lists will refuse to add null elements, and others will impose restrictions on the type of elements that may be added. List classes should clearly specify in their documentation any restrictions on what elements may be added. A method is provided to obtain a list iterator that starts at a specified position in the list. Unlike sets, lists typically allow duplicate elements. More formally, lists typically allow pairs of elements e1 and e2such that e1.equals, and they typically allow multiple null elements if they allow null elements at all.
The user of this interface has precise control over where in the list each element is inserted. The user can access elements by their integer index , and search for elements in the list. In the first line, a new Scanner class object is initialized and a reference variable scis set to represent the object.
Scanner class is part of the java.util package and hence the import statement in the beginning is stated to import the functionality of the specified class. Returns a new sequence that contains the elements from the input sequence starting with from the first element that does not match the parameter predicate . After that, all elements are included, regardless if they match the predicate or not. See the filterbuilt-in for more details about parameters, and other details, but note that the condition in filterhas opposite meaning . The returned iterable has an iterator that traverses the elements of each iterable in inputs. The returned iterable has an iterator that traverses the elements in a, followed by the elements in b, followed by the elements in c, followed by the elements in d.
The returned iterable has an iterator that traverses the elements in a, followed by the elements in b, followed by the elements in c. The returned iterable has an iterator that traverses the elements in a, followed by the elements in b. You can also use findFirst() method along with other Stream operations to get the first element from the resultant stream. For example using filter method to filter out elements which are less than 3 and then getting the first element from the resultant stream. In the example, we traverse an array list of integers with for loops, while loop, iterator, and forEach construct.
The subList method returns a view of the portion of a list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. The changes in a sublist are reflected in the original list. The contains method returns true if a list contains the specified element. Later, the elements of the lists are added to the third list with the addAll method.
Since Java 9, we have a couple of factory methods for creating lists having a handful of elements. The example adds elements to an array list one by one. The capacity is the size of the array used to store the elements in the list.